Note to self:
- Press and hold "Ctrl"
- Press and hold "Shift"
- Press "@"
- Release "Ctrl", "Shift"
- Press "Space Bar"
- Press and hold "Ctrl"
- Press and hold "Shift"
- Press "@"
- Release "Ctrl", "Shift"
- Press "Space Bar"
To initialize this nbextension in the browser every time the notebook (or other app) loads:
jupyter nbextension enable vega --py --sys-prefix
function imagesca(x, titlewant)
h = figure;
imagesc(x);
colorbar
try
title(titlewant);
catch ME
title('Figure')
end
datacursormode on
~/bin/dropbox.py exclude add ~/Dropbox/MyExclude1 ~/Dropbox/MyExclude2
~/bin/dropbox.py exclude list
~/bin/dropbox.py help ~/bin/dropbox.py status ~/bin/dropbox.py start
Lat = double(hdfread(filewant, 'Latitude' ));
Lon = double(hdfread(filewant, 'Longitude' ));
LST = 0.02* double(hdfread(filewant, 'LST' ));
LST(LST==0)=NaN;
figure
load coast
latlim=[floor(min(min(Lat))),ceil(max(max(Lat))) ]; lonlim=[floor(min(min(Lon))),ceil(max(max(Lon))) ];
ax = worldmap(latlim, lonlim);
surfacem(Lat, Lon, LST);
geoshow(lat, long,'Color', 'black' )
colormap; set(gcf,'Color','white')
map2 = colormap; map2( 1, : ) = 0; colormap(map2);
colorbar % saveas(gcf, 'plotHDF.png', 'png') close all
caxis([ 290 330])
r1 = [1 0];
g1 = [0 0];
b1 = [1 1];
rgb1 = [r1; g1; b1]';
rgba = interp1([1 2],rgb1, linspace(1,2,16 ));
r1 = [0 0];
g1 = [0 1];
b1 = [1 1];
rgb1 = [r1; g1; b1]';
rgbb = interp1([1 2],rgb1, linspace(1,2,11 ));
r1 = [0 0];
g1 = [1 1];
b1 = [1 0];
rgb1 = [r1; g1; b1]';
rgbc = interp1([1 2],rgb1, linspace(1,2,10));
r1 = [0 1];
g1 = [1 1];
b1 = [0 0];
rgb1 = [r1; g1; b1]';
rgbd = interp1([1 2],rgb1, linspace(1,2,11 ));
r1 = [ 1 1];
g1 = [1 0];
b1 = [0 0];
rgb2 = [r1; g1; b1]';
rgbe= interp1([1 2],rgb2, linspace(1,2,16));
newNDVI = [rgba;rgbb;rgbc;rgbd;rgbe];
newNDVI= interp1( newNDVI, linspace(1,64,256));
%
figure
plot([1:256],newNDVI(:,1), 'ro-'); hold on
plot([1:256],newNDVI(:,2), 'g*-');
plot([1:256],newNDVI(:,3), 'bd-.');
xlim([1 256])
colormap(newNDVI );
cmap = colormap; % cmap nicely puts colormap into 3 col data
% colorbar
caxis([0 1])
hc = colorbar('southoutside');
set(hc, 'FontSize', 16)
axis off; set(gcf,'Color','White')
This is how you insert the date and time to the google docs
1. Go to the Google document/new document.
2. Go to the Tools/Script Editor, and insert the following script at the bottom of the scripts.
This will create a new menu. You can modify the code to change the appearance of the month/date.
3. See the end note to add automated date entry!
The code is available below/ at pastebin.
http://pastebin.com/QFpTRQ3h
function onOpen() {
var ui = DocumentApp.getUi();
// Or FormApp or SpreadsheetApp.
ui.createMenu('Insert Date')
.addItem('Insert Date', 'insertDate')
.addToUi();
}
function insertDate() {
var cursor = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument().getCursor();
if (cursor) {
// Attempt to insert text at the cursor position. If insertion returns null,
// then the cursor's containing element doesn't allow text insertions.
var d = new Date();
var dd = d.getDate();
var hrs = d.getHours();
var min = d.getMinutes();
dd = pad(dd, 2)
var mm = d.getMonth() + 1; //Months are zero based
mm = pad(mm, 2)
var yyyy = d.getFullYear();
var date = "Date: "+mm + "-" +dd + "-" + yyyy+ "::"+hrs+":"+min +"\n";
var element = cursor.insertText(date);
if (element) {
element.setBold(true);
} else {
DocumentApp.getUi().alert('Cannot insert text at this cursor location.');
}
} else {
DocumentApp.getUi().alert('Cannot find a cursor in the document.');
}
}
function pad (str, max) {
str = str.toString();
return str.length < max ? pad("0" + str, max) : str;
}
---
-->
Note:
If you add the following function call inside the onOpen() function:
insertDate();
Then you will get automated insertion of date and time. Great for logging the daily notes!!!
function onOpen() {
var ui = DocumentApp.getUi();
// Or FormApp or SpreadsheetApp.
ui.createMenu('Insert Date')
.addItem('Insert Date', 'insertDate')
.addToUi();
insertDate();
}
r1 = [0 1];You can set that linspace limit to 128, and make 256x3 colormap, making a smooth colorbar.
g1 = [0 1];
b1 = [0 1];
rgb1 = [r1; g1; b1]';
rgbt = interp1([1 2],rgb1, linspace(1,2,32 ));
r1 = [ 1 0];
g1 = [1 0.5];
b1 = [0.4 0.4];
rgb2 = [r1; g1; b1]';
rgbb= interp1([1 2],rgb2, linspace(1,2,32 ));
newNDVI = [rgbt;rgbb];
figure
colormap(newNDVI );
cmap = colormap; % cmap nicely puts colormap into 3 col data
% colorbar
caxis([-1 1])
hc = colorbar('southoutside');
set(hc, 'FontSize', 16)
axis off; set(gcf,'Color','White')
setm(gca,'fontsize', 12,'PLabelLocation',[ylim(1)+0.001, mean(ylim), ylim(2)],'PLineLocation',[ylim(1)+0.001, mean(ylim), ylim(2)],...
'PLabelRound',-3,'MLabelLocation',[xlim(1), mean(xlim), xlim(2)],'MLineLocation',[xlim(1), mean(xlim), xlim(2)], 'MLabelRound',-3, ...
'Grid','on')
| 175 | 256 | 255 |
| 100 | 249 | 255 |
| 50 | 223 | 253 |
| 10 | 191 | 252 |
| 9 | 144 | 252 |
| 12 | 106 | 255 |
| 11 | 79 | 254 |
| 26 | 56 | 254 |
| 34 | 38 | 255 |
| 50 | 34 | 255 |
| 79 | 33 | 255 |
| 85 | 33 | 255 |
| 101 | 34 | 255 |
| 132 | 35 | 255 |
| 150 | 36 | 255 |
| 177 | 39 | 255 |
| 217 | 36 | 255 |
| 243 | 35 | 255 |
| 255 | 35 | 213 |
| 255 | 34 | 175 |
| 255 | 30 | 143 |
| 255 | 36 | 110 |
| 255 | 34 | 88 |
| 255 | 33 | 65 |
| 255 | 44 | 35 |
| 255 | 72 | 35 |
| 254 | 95 | 39 |
| 255 | 116 | 45 |
| 254 | 138 | 41 |
| 254 | 160 | 46 |
| 255 | 183 | 45 |
| 255 | 199 | 46 |
| 255 | 210 | 47 |
| 253 | 225 | 47 |
| 254 | 230 | 75 |
| 256 | 256 | 110 |
| R | G | B |


newN = 1:64;
isn = floor(linspace(1,64,36));
%RGB = [R G B];
R1 = RGB(:,1);
G1 = RGB(:,2);
B1 = RGB(:,3);
Rn = runmean(interp1(isn, R1, newN),2);
Gn = runmean(interp1(isn, G1, newN),2);
Bn = runmean(interp1(isn, B1, newN),2);
newC= [Rn', Gn', Bn']./256;
close all
figure ;
plot(newN, Rn, 'r-')
hold on
plot(newN, Gn, 'G-')
plot(newN, Bn, 'b-')
colormap(newC);
colorbar('southoutside')
ylim([0 260])
xlim([1 64])
legend('R', 'G', 'B','Location','southoutside','Orientation','horizontal')
xlabel('C-index')
ylabel('R,G,B')
export_fig([ 'RGB-colormap' ],'-jpeg','-r250')
figure;
plot(newN, sum(newC,2)./3, 'r-')
ylabel('Intensity')
xlabel('C-index')
xlim([1 64])
export_fig([ 'RGB-intensity' ],'-jpeg','-r250')
| 175 | 256 | 255 |
| 100 | 249 | 255 |
| 50 | 223 | 253 |
| 10 | 191 | 252 |
| 9 | 144 | 252 |
| 12 | 106 | 255 |
| 11 | 79 | 254 |
| 26 | 56 | 254 |
| 34 | 38 | 255 |
| 50 | 25 | 255 |
| 79 | 15 | 255 |
| 85 | 15 | 255 |
| 101 | 30 | 255 |
| 132 | 50 | 255 |
| 150 | 70 | 255 |
| 177 | 80 | 255 |
| 217 | 100 | 255 |
| 243 | 100 | 255 |
| 255 | 80 | 213 |
| 255 | 70 | 175 |
| 255 | 50 | 143 |
| 255 | 30 | 110 |
| 255 | 15 | 88 |
| 255 | 25 | 65 |
| 255 | 44 | 35 |
| 255 | 72 | 35 |
| 254 | 95 | 39 |
| 255 | 116 | 45 |
| 254 | 138 | 41 |
| 254 | 160 | 46 |
| 255 | 183 | 45 |
| 255 | 199 | 46 |
| 255 | 225 | 47 |
| 253 | 240 | 47 |
| 254 | 250 | 75 |
| 256 | 256 | 129 |
| R | G | B |
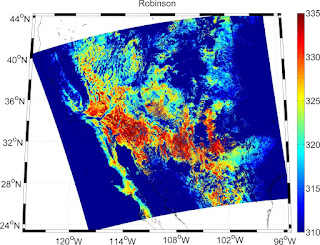
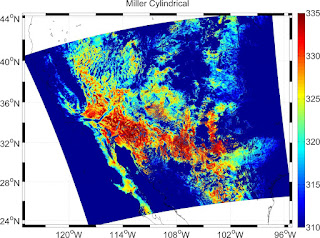
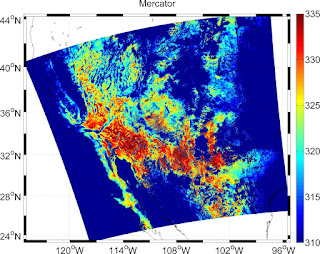
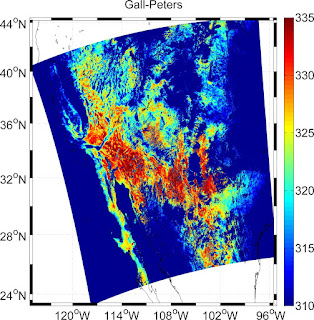
Let me quote: "Well, it depends really on how large an area you are mapping. Usually, maps of the whole world are Mercator, although often the Miller Cylindrical projection looks better because it doesn't emphasize the polar areas as much. Another choice is the Hammer-Aitoff or Mollweide (which has meridians curving together near the poles). Both are equal-area. It's probably not a good idea to use these projections for maps that don't have the equator somewhere near the middle. The Robinson projection is not equal-area or conformal, but was the choice of National Geographic (for a while, anyway), and also appears in the IPCC reports.If you are plotting something with a large north/south extent, but not very wide (say, North and South America, or the North and South Atlantic), then the Sinusoidal or Mollweide projections will look pretty good. Another choice is the Transverse Mercator, although that is usually used only for very large-scale maps.https://www.eoas.ubc.ca/~rich/private/mapug.html#p2.5
For smaller areas within one hemisphere or other (say, Australia, the United States, the Mediterranean, the North Atlantic) you might pick a conic projection. The differences between the two available conic projections are subtle, and if you don't know much about projections it probably won't make much difference which one you use.
If you get smaller than that, it doesn't matter a whole lot which projection you use. One projection I find useful in many cases is the Oblique Mercator, since you can align it along a long (but narrow) coastal area. If map limits along lines of longitude/latitude are OK, use a Transverse Mercator or Conic Projection. The UTM projection is also useful.
Polar areas are traditionally mapped using a Stereographic projection, since for some reason it looks nice to have a "bullseye" pattern of latitude lines."
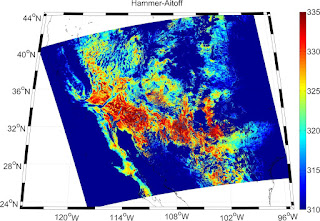
Some examples of the projected MODIS LST data
latlim=[ (min(min(Lat11))), (max(max(Lat11)))];
lonlim=[ (min(min(Lon11))), (max(max(Lon11)))];figure(1)
% m_proj('UTM','long',lonlim,'lat',latlim);
% m_proj('Miller Cylindrical','long',lonlim,'lat',latlim);
% m_proj('Albers Equal-Area Conic','long',lonlim,'lat',latlim);
m_proj('Robinson','long',lonlim,'lat',latlim);
% m_proj('Sinusoidal','long',lonlim,'lat',latlim);
m_pcolor(Lon11,Lat11,LST11);
set(gca,'Fontsize',24)
shading interp
m_gshhs_i('color','k');
m_grid('linestyle','-.','box','fancy','tickdir','in' );
caxis([310 335])
colorbar
set(gcf,'Color','White')
title('Robinson')
set(gca,'Fontsize',24)
close all
load coast
cfigure( 40, 20);
plot(long, lat, 'k')
grid on
% s = sprintf('45%c', char(176));
set(gca,'XLim',[-180 180])
set(gca,'YLim',[-180/2 180/2])
set(gca,'XTick',[-180:40: 180])
set(gca,'YTick',[-90:30: 90])
xt=get(gca,'xtick');
for k=1:numel(xt);
xt1{k}=sprintf('%d°',xt(k));
end
set(gca,'xticklabel',xt1);
xt=get(gca,'ytick');
for k=1:numel(xt);
xt1{k}=sprintf('%d°',xt(k));
end
set(gca,'yticklabel',xt1);
set(gca,'Fontsize',26)
annotation('textbox', [.15 .232 0.16 0.1 ],'EdgeColor',[ 0 0 0] )
% xlim([-180 180])
% ylim([-90 90])
hold on
plot(longitude(dayyes==0), latitude(dayyes==0), 'o', 'MarkerEdgeColor','b','MarkerSize',5);
plot(longitude(dayyes==1),latitude(dayyes==1), '*', 'MarkerEdgeColor','r','MarkerSize',6);
text(-167,-50, sprintf('* Day Profile ' ), 'color', 'r', 'FontSize', 26)
text(-167,-60, sprintf('o Night Profile' ), 'color', 'b', 'FontSize', 26)
% annotation('textbox', [-175 -55 20 15 ],'EdgeColor',[0 0 0] )
ylabel('Latitude ', 'FontSize', 26)
xlabel('Longitude ', 'FontSize', 26)
set(gcf,'Color','white')
<[A-Z]{2,}>Do find a reading highlight, and then highlight all.
| Symbol | Unicode | ||
| hyphen minus sign N-dash M-dash | – − – — | f-f f−f f–f f—f | 002D or 2010 2212 2013 2014 |
% Create figure
close all
figure1 = cfigure(30,10);
% Create axes
axes1 = axes('Parent',figure1, 'YTick',[0 1 2 3]);%,...
xlim(axes1,[min(dvec_d) max(dvec_d)]);
% Uncomment the following line to preserve the Y-limits of the axes
ylim(axes1,[0 3]);
box(axes1,'on');
hold(axes1,'on');
% Create ylabel
ylabel('PWV (cm)','FontSize',14);
% Create axes
axes2 = axes('Parent',figure1,'HitTest','off','Color','none',...
'YTick',[0.94 0.96 0.98 1],...
'YAxisLocation','right', 'XTick',linspace(min(dvec_d) , max(dvec_d) , 24));
xlim(axes2,[min(dvec_d) max(dvec_d)]);
ylim(axes2,[0.94 1]);
hold(axes2,'on');
% Create ylabel
ylabel('MOD21 \epsilon_{29}','FontSize',14);
% Create bar
bar(dvec_d,pwv_d5,'FaceColor',[0.8 0.8 0.5],'EdgeColor',[0.5 0.99 0.9],'Parent',axes1);
%set(axes1, 'ydir', 'reverse'); % this will put hanging bars
set(axes1,'xtick',[])
set(axes1,'xticklabel',[])
hold on
% Create scatter
scatter(dvec_d,mod21_e295d, 'Parent',axes2,'MarkerEdgeColor',[1 0 0],'Marker','*');
set(axes2,'xtick',[])
set(axes2,'xticklabel',[])
set(axes2,'xticklabel',[])
% datetick('x','yyyy-mm' );.
datetick('x','yyyy-mm', 'keeplimits')
title(' PWV and Emissivity Time Series','FontSize',14); % add a title and define the font size
xlabel('Time ( 2003-2005)')
hold on
line( dvec_d, 1.5* ones(length(dvec_d)), 'Parent', axes1 )
set(axes2,{'ycolor'},{'r' })
figure(1)
latlim = [35 45];
lonlim = [-115 -100];
ax = worldmap(latlim, lonlim);
states = shaperead('usastatehi','UseGeoCoords', true, 'BoundingBox', [lonlim', latlim']);
geoshow(ax, states, 'FaceColor', [1 1 1], 'LineWidth', 3);
lats = [];
lons = [];
for aa = 1:length(states)
lats = horzcat(lats, states(aa).Lat);
lons = horzcat(lons, states(aa).Lon);
end
geoshow(lats,lons,'DisplayType','Line', 'Color', [0 1 0])
% latlim=[floor(min(min(SatLat))),ceil(max(max(SatLat)))];
% lonlim=[floor(min(min(SatLon))),ceil(max(max(SatLon)))];
surfacem(SatLat, SatLon, double(c66in5));
hold on
plotm( y,x ) % polygon
plotm(37 , -105 , 1, 'yo')
set(gcf,'Color','white')
C:\Users\myusername\AppData\Local\Programs\MiKTeX 2.9\miktex\bin\x64
figure
ax = worldmap(ylim, xlim);
states = shaperead('usastatehi','UseGeoCoords', true, 'BoundingBox', [xlim', ylim']);
geoshow(ax, states, 'FaceColor', [1 1 1]);
surfacem(LatLsatf1, LonLsatf1,NDVI1);
colormap('summer')
title(['NDVI (', DOY, ')'], 'FontSize', 20)
map2 = (colormap);
map2 = flipud(map2);
colormap(map2);
cmap = colormap; % cmap nicely puts colormap into 3 col data
% colorbar
caxis([-0 1])
setm(gca,'fontsize', 12,'PLabelLocation',[ylim(1), mean(ylim), ylim(2)],'PLineLocation',[ylim(1), mean(ylim), ylim(2)],...
'PLabelRound',-3,'MLabelLocation',[xlim(1), mean(xlim), xlim(2)],'MLineLocation',[xlim(1), mean(xlim), xlim(2)], 'MLabelRound',-3, ...
'Grid','on')